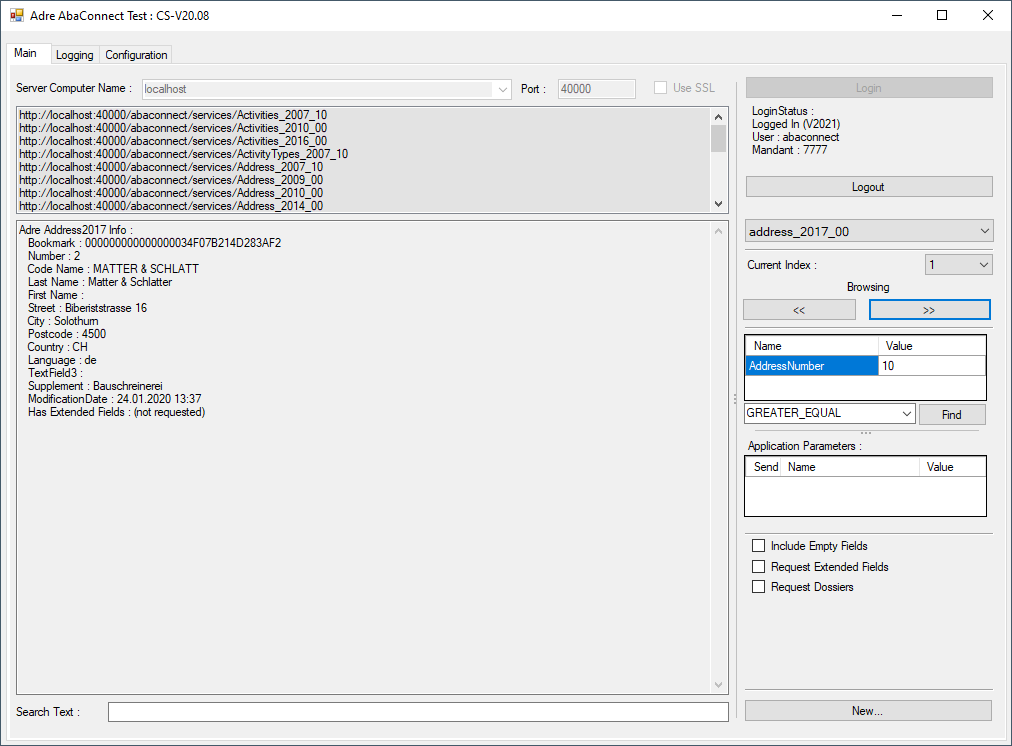
| UI-Area |
Description |
| Server Name and Port |
The name and port of the Abacus server computer can be entered. This changes the
URL for the desired ABACUS Server computer. Default is localhost. The server name and port number can be changed before the login.
The port number corresponds to the Abacus AbaWebServer (or AbaSioux) which is shown in the ABACUS ServiceManager. Default is 40000. |
| Interface URLs |
This field displays the current URL of the interfaces implemented in the
example. Changes to the computer server name or port number will be shown here. |
| Information Area |
This field displays the current interface data returned via the find
methods for the currently selected interface. |
| Search Input |
A search text can be entered and the text found in the Information panel will be highlighted
when Enter is pressed or when the Information panel is refreshed. |
| Login / Logout |
Click the login after setting the computer server name and port number. A login dialog
will be shown, where the Username, Password and Mandant number can be entered. After a successful login, the
login status is shown below the login button. Click to logout button to logout. The user will also be automatically logged out when the example application closes. |
Interface Selection /
Find Index |
Selects the current interface for the operations of find and save.
The combo box contains a list of the interface names listed in the Interface URLs.
The Find Index used for browsing and find-request can be selected
for the actual interface. The Find Index defines the data record sorting order, and defines the available Find-Parameters. |
| Browsing |
Browses through the selected interface with FIRST, NEXT, LAST or PRIOR, using
the Bookmark of the previous data record. If no previous data is available, a find FIRST or LAST will be
executed. The returned data will be displayed in the Information Area. Some of the interfaces allow
the index (i.e. sorting order of records) for the browsing to be selected in the current index list box
(e.g. in Address Index=1 sorts by address number and index=4 sorts by Name) |
| Find |
Depending on the interface and what is implemented in the example
application it may be possible to execute a Find for a selected interface. Specific parameters can be
entered into the Find parameter table. Click Find to execute the find operation with the entered values. The possible input
values for the find depend on the selected interface and what is implemented in the example. Generally, the Find.GREATER_EQUAL and Find.EQUAL
can be selected from the Find-Operation drop down list.
|
| Application Parameters |
Depending on the selected interface, application parameters may be available and can be selected
and sent with the requests. Each application parameter can be selected individually. The application parameters are normally optional. Application parameters
may only have an effect for import or export of data. Consult the further AbaConnect documenatation to determine if the parameter is required for import or export.
|
| Additional Parameters |
Many AbaConnect interfaces support additional parameters for
including Extended Field, Dossiers, or empty elements by the Find requests. If the interface supports these features they can normally
be selected via the checkbox, if the current interface supports such features. |
| New/Save |
Many of the examples also implement the save/new for a selected
interface. The Save button may be inactive if it is not available or implemented in the example. The example source code can be
inspected to see what is implemented. For a few interfaces other button or options may be shown in this area, depending
on the functionality that is implemented in the example (e.g. delete or update) |