Abacus REST-API
The Abacus REST-API provides access to various REST WebService interfaces. The Abacus REST-API is designed for access using a Service-User
that can be configured in the Abacus User Management. Q981, or in in Q910 for Abacus API's for application specific Entity Endpoints. A Service-User can only access Abacus
via the available interfaces (access to the Abacus UI is not possible).
The Service-Users are identified with a Client-ID and Client-Secret (Clientschlüssel), that can be copied from the Abacus User Management when the user is created.
Note: To create a Service-User for accessing the Abacus API (Rest-API's) for the application specific Entity Endpoints, please refer to the Program Q910. The API authentication process
described below is also valid for Service-Users created via Q910.
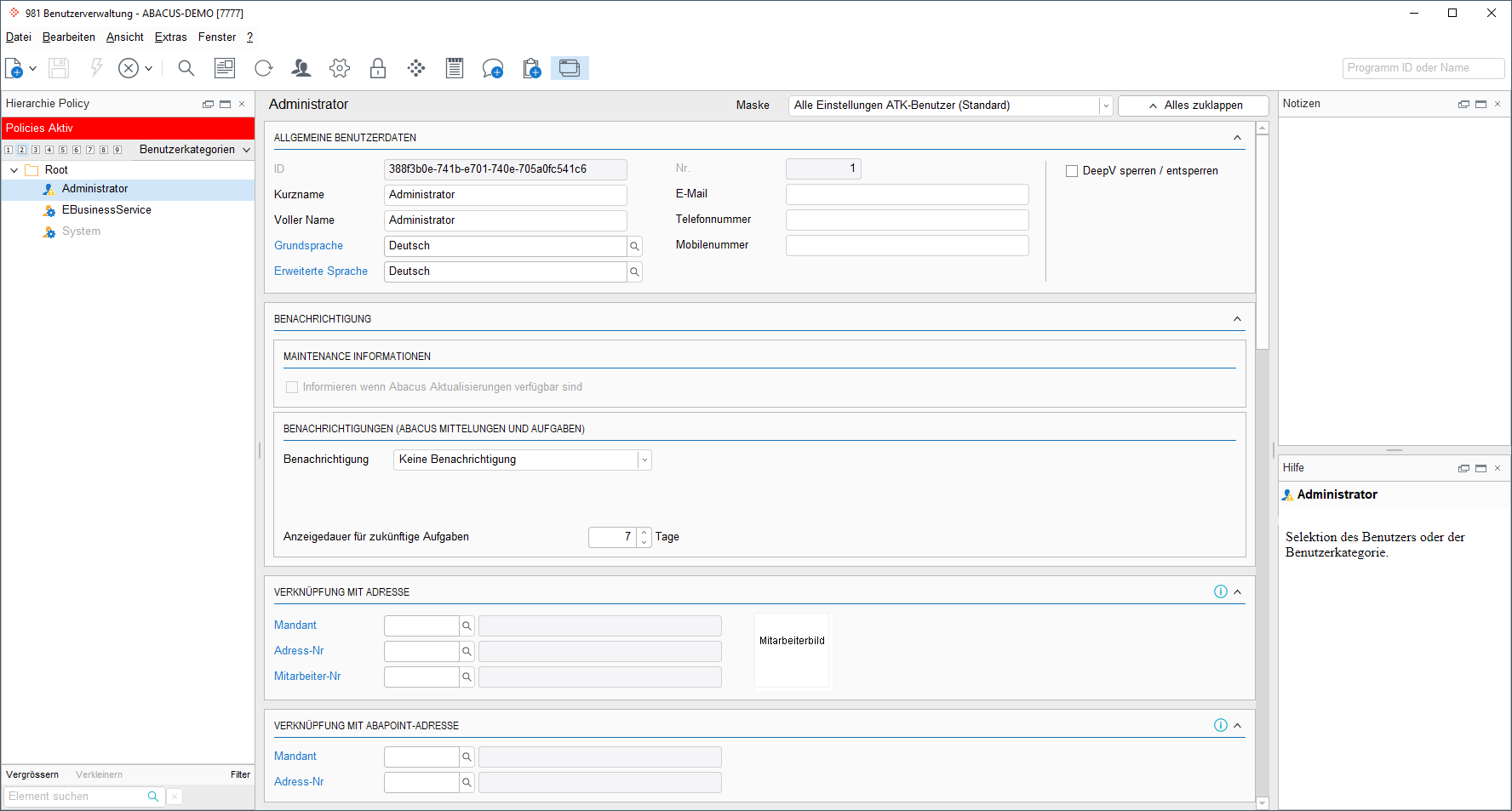
Setup of the Service User in Abacus UI (Q981)
The Abacus REST-API interfaces require a Service User that is configured in the Abacus User Management. The following general information shows how the service user can be created and configured in the Abacus User Management (Q981).
Note: Clicking with the mouse on the right (or left) half of the image will advance (or step back) through the various UI steps for creating a Service User.
>>
<<
|
|
|
|
It is important to copy the Client-Secret (Clientschlüssel) for the Service User during the creation of the User. The Client-Secret is only shown directly after the generation and will not be displayed again in the User Interface. A new Client-ID can be generated in the User Management with the "Passwort ändern" button. Directly after the new Client-Secret is generated, the value will be displayed. Thereafter the Client-Secret will no longer be displayed in the USer Manangement UI. It is not possible to obtain the current Client-Secret. If the Client-Secret is lost or no longer known, a new Client-Secret must be generated.
User Authentication via REST-API
The Service User can be used using OAuth to register (login) via the REST-API. This technique requires several standard steps, that are common for various OAuth authentications.
the Service User Client-ID and Client-Secret are required for the OAuth authenication.
Obtaining the Abacus Token-Endpoint
The Token-Endpoint can be obtained via the Abacus .well-known/openid-configuration URL. This returns a Token-Endpoint where the Access-Token for a specified Service-User can be requested.
Example Request:
GET /.well-known/openid-configuration HTTP/1.1
Accept-Charset: UTF-8
Accept: application/json
User-Agent: Java/11.0.6
Host: localhost:40000
Connection: keep-alive
Example Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Feature-Policy: camera 'none'; microphone 'none'; geolocation 'none'; speaker 'self'; fullscreen *
Server: Jetty(9.4.30.v20200611)
Cache-Control: no-store
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 738
{
"token_endpoint_auth_signing_alg_values_supported":["RS256"],
"token_revocation_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/token/revocation",
"jwks_uri":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/certs",
"end_session_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/auth/logout",
"id_token_signing_alg_values_supported":["RS256"],
"registration_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/api/oauth2-clients/v1/registration",
"scopes_supported":["abacus.pad", "openid", "email", "profile", "offline_access"],
"issuer":"http://localhost:40000",
"authorization_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/auth",
"token_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/token",
"userinfo_endpoint":"http://localhost:40000/oauth/oauth2/v1/user/userinfo"
}
Note: The "token_endpoint" will rarely change, but the webservice client implementation should always obtain the current token_endpoint so that if changes occur, the client program continues to operate correctly.
Obtaining the Abacus User Access-Token
The Service User Access-Token can be obtained via the Token-Endpoint URL from the previous step. There are various ways of passing the Client-ID and Client-Secret in the request to obtain the Access-Token.
- The Client-ID and Client-Secret can be hashed in a Basic Authorization HTTP Header key using Base64 (recommended)
- The Client-ID and Client-Secret can be included as part of the request payload
Example Request with Authorization Header :
Example : Client-ID:Client-Secret als Base64
Authorization: Basic Base64[<Client-ID>:<Client-Secret>]
POST /oauth/oauth2/v1/token HTTP/1.1
Accept-Charset: UTF-8
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Basic OTAzZDQwMTctZmE5NS1lYTAxLTg2YjQtZjg1OTcxMjllZmJhOjIxYWM0MWVkLTA5OTctODE0OC1jNzM5LTU5Y2RhMDkxZTg3Nw==
User-Agent: Java/11.0.6
Host: localhost:40000
Accept: text/html, image/gif, image/jpeg, *; q=.2, */*; q=.2
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 29
grant_type=client_credentials
Example Request with Client-ID and Client-Secret in Request payload :
POST /oauth/oauth2/v1/token HTTP/1.1
Accept-Charset: UTF-8
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: Java/11.0.6
Host: localhost:40000
Accept: text/html, image/gif, image/jpeg, *; q=.2, */*; q=.2
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 127
client_id=<Client-ID>&client_secret=<Client-Secret>&grant_type=client_credentials
Example Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
X-Frame-Options: deny
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Feature-Policy: camera 'none'; microphone 'none'; geolocation 'none'; speaker 'self'; fullscreen *
Server: Jetty(9.4.30.v20200611)
Content-Security-Policy: default-src https: 'self'; img-src https: data: 'self'; frame-src 'self'; font-src https: data: 'self';
Cache-Control: no-store
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 774
{
"access_token":"eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjEiLCJ0eXAiOiJKV1QifQ...[abbreviated for display]...JFLh2RDzq-1aWN9X8waFvLskedjcLS5lOoeD7xIw",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":600
}
The Access-Token (Type : "Bearer") is returned in the response. The access_token is valid for specified period of time (e.g. 600 seconds - 10 Minutes), after which a new Access-Token should be obtained. A access_token should be used for the duration of the valid time (or shortly before). A new Access-Token should not be created for each request. There is no requirement to logout.
Using the Abacus REST-API's
After obtaining the access-token via the OAuth-Endpoint, the REST-API interfaces can be accessed by including the Authorization header with the specific request. Further information regarding the Abacus REST-API's can be located directly in the Abacus Server with the Swagger URL http://localhost:40000/swagger-ui/index.html.

